Product Description
Production Process: sand casting, lost wax casting, CNC precision machining
Part Weight: 1.2-33.4kg
Material:Gray Iron, HT200,HT25,HT300,HT350 GG14,GG20,GG25,GG30
EN-GJS-150, EN-GJS-200, EN-GJS-250, EN-GJS-300
ASTM A48 class 25, class 30, class 40, class 50, class 60
Ductile Iron(Nodular Iron):QT400, QT450, QT500, QT600, GGG40, GGG50, GGG60
60-40-18, 65-45-12, 70-50-01, 80-60-03
Alloy Steel:1571, 1045, 4140, WCB, LCB
Stainless Steel:SS304, SS304L, SS316, SS316L, CF8M, CF-8,
Casting Tolerance: CT9-CT11, CT4-CT7
Machining Tolerance: IT4-IT12
| PROCESS | MATERIAL | STHangZhouRD | |
| SAND CASTING |
Green Sand | Grey Iron, Ductile Iron, Malleable Iron, Stanless Steel, Carbon, Steel, Aluminium | ASTM BS JIS DIN etc |
| Furan Resin Sand | |||
| Cold Harden Resin Sand | |||
| INVESTMENT CASTING |
Sodium Silicone (Water galss) | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Special Alloy Steel Aluminum | |
| Silica Sol | |||
| FORGING | Hammer Forging | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Streel, Aluminum | |
| Die Forging | |||
| Roll Forging | |||
| STAMPING MACHINING | STAMPING MACHINING | All metal material | |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | Low Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | High Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Double Acting |
| Working Method: | Rotary |
| Adjusted Form: | Switching Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do hydraulic cylinders contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of industrial processes?
Hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in enhancing the overall cost-effectiveness of industrial processes. They offer several advantages and contribute to increased productivity, improved efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced operational performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders contribute to the cost-effectiveness of industrial processes:
1. High Power Density:
– Hydraulic cylinders provide a high power-to-weight ratio, allowing them to generate substantial force in a compact design. This power density enables the use of smaller and lighter equipment, reducing material and manufacturing costs, and increasing the efficiency of industrial processes.
2. Precise Force and Position Control:
– Hydraulic cylinders offer precise force and position control, allowing for accurate movement and positioning of machinery or workpieces. This level of control enhances process efficiency, reduces material waste, and improves overall product quality. Precise force control also minimizes the risk of equipment damage, further reducing maintenance and repair costs.
3. High Load Handling Capacity:
– Hydraulic cylinders are known for their ability to handle high loads. They can exert significant force, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. By efficiently handling heavy loads, hydraulic cylinders contribute to increased productivity and throughput, reducing the need for additional equipment and streamlining industrial processes.
4. Flexibility and Versatility:
– Hydraulic cylinders offer a high degree of flexibility and versatility in industrial processes. They can be easily integrated into various types of machinery and equipment, allowing for diverse applications. This adaptability reduces the need for specialized equipment, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
5. Energy Efficiency:
– Hydraulic systems, including hydraulic cylinders, can be designed to operate with high energy efficiency. By utilizing efficient hydraulic circuit designs, advanced control systems, and energy recovery mechanisms, hydraulic cylinders minimize energy waste and reduce operational costs. Energy-efficient hydraulic systems also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly industrial operation.
6. Durability and Longevity:
– Hydraulic cylinders are built to withstand demanding industrial environments and heavy usage. They are constructed with robust materials and undergo stringent quality control measures to ensure durability and longevity. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions and repetitive motion reduces the need for frequent replacements, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
7. Reduced Maintenance Requirements:
– Hydraulic cylinders require relatively low maintenance compared to other types of actuators. Properly designed hydraulic systems with efficient filtration and contamination control mechanisms can prevent damage to the cylinders and extend their service life. Reduced maintenance requirements result in lower downtime, decreased labor costs, and improved cost-effectiveness of industrial processes.
8. System Integration and Automation:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be seamlessly integrated into automated industrial processes. By incorporating hydraulic cylinders into automated systems, tasks can be performed with precision and repeatability, reducing human error and optimizing efficiency. Automation also allows for continuous operation, increasing productivity and overall cost-effectiveness.
9. Cost-Effective Replacement:
– In situations where hydraulic cylinders require replacement or repair, the cost-effectiveness of the process is still maintained. Hydraulic cylinders are typically modular in design, allowing for easy replacement of individual components or complete units. This modularity reduces downtime and associated costs, as only the affected components need to be replaced, rather than the entire system.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of industrial processes through their high power density, precise control capabilities, high load handling capacity, flexibility, energy efficiency, durability, reduced maintenance requirements, system integration, and cost-effective replacement options. Their ability to enhance productivity, efficiency, and operational performance while minimizing maintenance and downtime costs makes hydraulic cylinders a valuable component in various industrial applications.

Handling the Challenges of Minimizing Fluid Leaks and Contamination in Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders face challenges when it comes to minimizing fluid leaks and contamination, as these issues can impact the performance, reliability, and lifespan of the system. However, there are several measures and design considerations that help address these challenges effectively. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination:
- Sealing Systems: Hydraulic cylinders employ advanced sealing systems to prevent fluid leaks. These systems typically include various types of seals, such as piston seals, rod seals, and wiper seals. The seals are designed to create a tight and reliable barrier between the moving components of the cylinder and the external environment, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage.
- Seal Material Selection: The choice of seal materials is crucial in minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. Hydraulic cylinder manufacturers carefully select seal materials that are compatible with the hydraulic fluid used and resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemical degradation. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the seals, reducing the likelihood of leaks or premature seal failure.
- Proper Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance of hydraulic cylinders is essential for minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. During installation, attention should be given to proper alignment, torqueing of bolts, and adherence to recommended procedures. Regular maintenance includes inspecting seals, replacing worn-out components, and addressing any signs of leakage promptly. Proper maintenance practices help identify and rectify issues before they escalate and cause significant problems.
- Contamination Control: Hydraulic cylinders incorporate measures to control contamination and maintain fluid cleanliness. This includes the use of filtration systems, such as in-line filters, to remove particles and contaminants from the hydraulic fluid. Additionally, hydraulic reservoirs often have breathers and desiccant filters to prevent moisture and airborne contaminants from entering the system. By controlling contamination, hydraulic cylinders minimize the risk of damage to internal components and maintain optimal system performance.
- Environmental Protection: Hydraulic cylinders may be equipped with protective features to safeguard against external contaminants. For example, bellows or protective boots can be installed to shield the rod and seals from debris, dirt, or moisture present in the operating environment. These protective measures help extend the life of the seals and enhance the overall reliability of the hydraulic cylinder.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders employ sealing systems, appropriate seal materials, proper installation and maintenance practices, contamination control measures, and environmental protection features to handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. By implementing these measures, manufacturers can ensure reliable and long-lasting hydraulic cylinder performance, minimize the risk of fluid leakage, and maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic system.
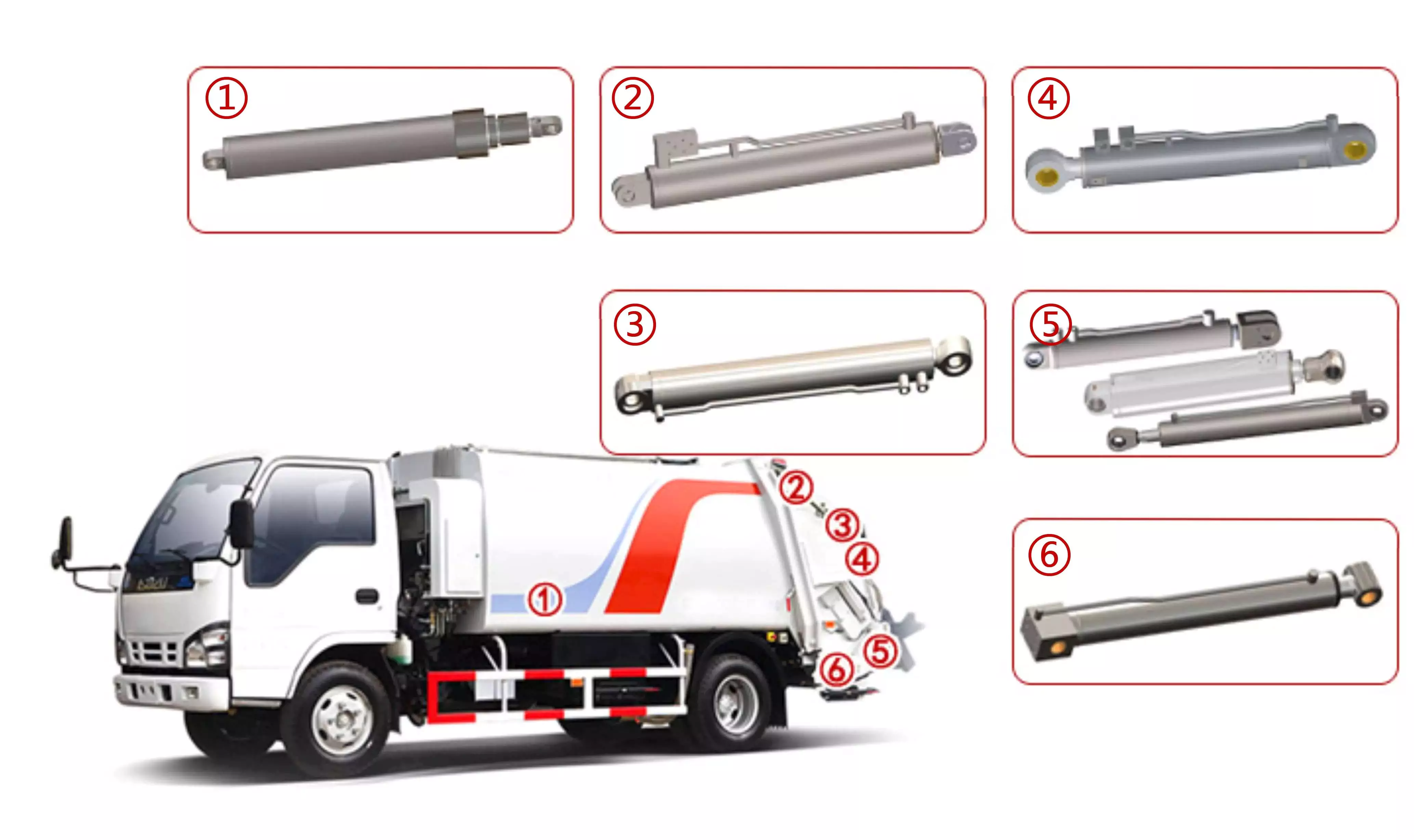

How do hydraulic cylinders accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements?
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements, providing flexibility and adaptability for different applications. They can be tailored to meet specific needs by considering factors such as piston diameter, rod diameter, hydraulic pressure, and cylinder design. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements:
1. Cylinder Size and Design:
– Hydraulic cylinders come in various sizes and designs to accommodate different stroke lengths and force requirements. The cylinder’s diameter, piston area, and rod diameter are key factors that determine the force output. Larger cylinder diameters and piston areas can generate greater force, while smaller diameters are suitable for applications requiring lower force. By selecting the appropriate cylinder size and design, stroke lengths and force requirements can be effectively accommodated.
2. Piston and Rod Configurations:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be designed with different piston and rod configurations to accommodate variations in stroke length. Single-acting cylinders have a single piston and can provide a stroke in one direction. Double-acting cylinders have a piston on both sides, allowing for strokes in both directions. Telescopic cylinders consist of multiple stages that can extend and retract, providing a longer stroke length compared to standard cylinders. By selecting the appropriate piston and rod configuration, the desired stroke length can be achieved.
3. Hydraulic Pressure and Flow:
– The hydraulic pressure and flow rate supplied to the cylinder play a crucial role in accommodating variations in force requirements. Increasing the hydraulic pressure increases the force output of the cylinder, enabling it to handle higher force requirements. By adjusting the pressure and flow rate through hydraulic valves and pumps, the force output can be controlled and matched to the specific requirements of the application.
4. Customization and Tailoring:
– Hydraulic cylinders can be customized and tailored to meet specific stroke length and force requirements. Manufacturers offer a wide range of cylinder sizes, stroke lengths, and force capacities to choose from. Additionally, custom-designed cylinders can be manufactured to suit unique applications with specific stroke length and force demands. By working closely with hydraulic cylinder manufacturers, it is possible to obtain cylinders that precisely match the required stroke length and force requirements.
5. Multiple Cylinders and Synchronization:
– In applications that require high force or longer stroke lengths, multiple hydraulic cylinders can be used in combination. By synchronizing the movement of multiple cylinders through the hydraulic system, the stroke length and force output can be effectively increased. Synchronization can be achieved using mechanical linkages, electronic controls, or hydraulic circuitry, ensuring coordinated movement and force distribution across the cylinders.
6. Load-Sensing and Pressure Control:
– Hydraulic systems can incorporate load-sensing and pressure control mechanisms to accommodate variations in force requirements. Load-sensing systems monitor the load demand and adjust the hydraulic pressure accordingly, ensuring that the cylinder delivers the required force without exerting excessive force. Pressure control valves regulate the pressure within the hydraulic system, allowing for precise control and adjustment of the force output based on the application’s needs.
7. Safety Considerations:
– When accommodating variations in stroke length and force requirements, it is essential to consider safety factors. Hydraulic cylinders should be selected and designed with an appropriate safety margin to handle unexpected loads or variations in operating conditions. Safety mechanisms such as overload protection valves and pressure relief valves can be incorporated to prevent damage or failure in situations where the force limits are exceeded.
By considering factors such as cylinder size and design, piston and rod configurations, hydraulic pressure and flow, customization options, synchronization, load-sensing, pressure control, and safety considerations, hydraulic cylinders can effectively accommodate variations in stroke length and force requirements. This flexibility allows hydraulic cylinders to be tailored to meet the specific demands of a wide range of applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.

editor by CX 2023-10-14