Product Description
hydraulic cylinder for hydraulic press machine
Product Description
1.Piston rod electroplate hard chrome;
2.lighter and easier to maintenance double acting hydraulic cylinder;
3.High quality alloy seamless steel pipe have better mechanical properties;
4.The world famous brands of seals, such as Parker, Merkel, Hallite, Kaden, etc;
5.World-class processing technology ensures stable and reliable quality.
| NO | ITEM | DATA of double acting hydraulic cylinder |
| 1 | Material | Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, 27SiMn,45#,20#,etc |
| 2 | Honed tube | 40-300mm, Heat treatment, honing, rolling |
| 3 | Honed tube | 30-280mm, plated nickel or hard Chrome or ceramic |
| 4 | Seal kit | Parker, Merkel, Hallite, Kaden, etc |
| 5 | Coating | Sandblasting, primer paint, middle paint, finish paint, Color can paint according to customer demands. |
| 6 | Technology | double acting hydraulic cylinder |
| 7 | Mounting type | Pin-eye |
| 8 | Working medium | Hydraulic Oil |
| 9 | Working pressure | 16-20Mpa press hydraulic cylinder |
| 10 | Temperature range | -50°C to +100°C |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
Tsingshi hydraulic is a hydraulic telescopic cylinder for dump tipper truck company which takes up with hydraulic design, R&D, manufacturer, sell and service hydraulic products-hydraulic press cylinder.
-hydraulic cylinder for press Certification ISO9001 TS16949, etc;
-shop press hydraulic cylinder Export to North America, South America, Australia, South Korea, Southeast Asia, South Africa, Europe, Middle East, etc;
-ODM&OEM mini double acting hydraulic cylinder according to client’s requirements;
-Professional manufacturer& supplier of Hydraulic Cylinders over 30 years;
-The press double acting hydraulic cylinder can be used for hydraulic press etc;
CUSTOMERS PHOTOS
QUALITY GUARANTEE
HIGH QUALITITY GUARANTEE-double acting hydraulic cylinder
-7*24 service.
-Competitive price.
-Professional technical team.
-Perfect after-sales service system.
-ODM&OEM Hydraulic Cylinder according to customer needs.
-Strong Hydraulic Cylinder production capacity to ensure fast delivery.
-Guarantee Quality. Every process must be inspected, all products need be tested before leaving the factory.
<hydraulic cylinder Leak Test
<hydraulic cylinder press Buffer Test
<cylinder hydraulic press Reliability Test
<hydraulic power press cylinder Full Stroke Test
<hydraulic shop press cylinder Operation Test
<hydraulic press cylinder Pressure Tight Test
<hydraulic cylinder for press Load Efficiency Test
<press hydraulic cylinder Start-up Pressure Test
<double acting hydraulic cylinder Testing the Effect of Limit
SALES AND SERVICE
PRODUCTS SERIES
ONE WORLD ONE LOVE
| Certification: | CE, ISO/Ts16949 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | Medium Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | Normal Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Double Acting |
| Working Method: | Straight Trip |
| Adjusted Form: | Regulated Type |
| Samples: |
US$ 2000/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
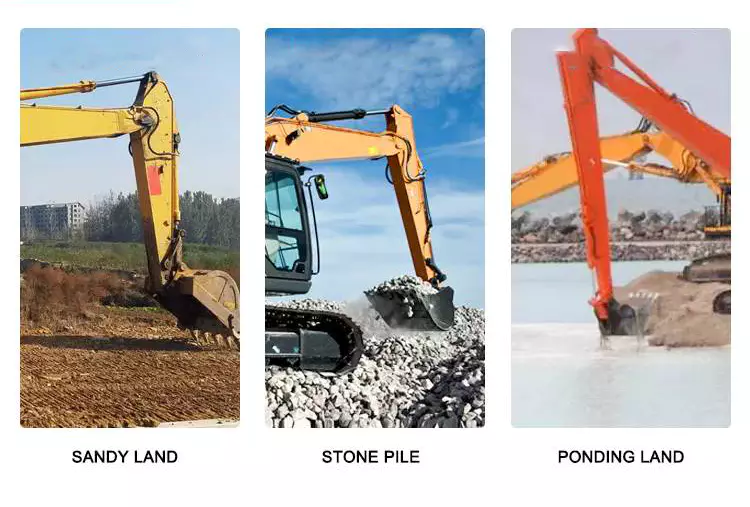

What advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have improved sealing and reliability?
Advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have continuously contributed to improving sealing and reliability in hydraulic systems. These advancements aim to address common challenges such as leakage, wear, and failure of seals, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are several key advancements that have significantly improved sealing and reliability in hydraulic cylinders:
1. High-Performance Sealing Materials:
– The development of advanced sealing materials has greatly improved the sealing capabilities of hydraulic cylinders. Traditional sealing materials like rubber have been replaced or enhanced with high-performance materials such as polyurethane, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), and various composite materials. These materials offer superior resistance to wear, temperature, and chemical degradation, resulting in improved sealing performance and extended seal life.
2. Enhanced Seal Designs:
– Advancements in seal designs have focused on improving sealing efficiency and reliability. Innovative seal profiles, such as lip seals, wipers, and scrapers, have been developed to optimize fluid retention and prevent contamination. These designs provide better sealing performance, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage and maintaining system integrity. Additionally, improved seal geometries and manufacturing techniques ensure tighter tolerances, reducing the potential for seal failure due to misalignment or extrusion.
3. Integrated Seal and Bearing Systems:
– Hydraulic cylinders now incorporate integrated seal and bearing systems, where the sealing elements also serve as bearing surfaces. This design approach reduces the number of components and potential failure points, improving overall reliability. By integrating seals and bearings, the risk of seal damage or displacement due to excessive loads or misalignment is minimized, resulting in enhanced sealing performance and increased reliability.
4. Advanced Coatings and Surface Treatments:
– The application of advanced coatings and surface treatments to hydraulic cylinder components has significantly improved sealing and reliability. Coatings such as chrome plating or ceramic coatings enhance surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. These surface treatments provide a smoother and more durable surface for seals to operate against, reducing friction and improving sealing performance. Moreover, specialized coatings can also provide self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for additional lubrication and enhancing reliability.
5. Sealing System Monitoring and Diagnostic Technologies:
– The integration of monitoring and diagnostic technologies in hydraulic systems has revolutionized seal performance and reliability. Sensors and monitoring systems can detect and alert operators to potential seal failures or leaks before they escalate. Real-time monitoring of pressure, temperature, and seal performance parameters allows for proactive maintenance and early intervention, preventing costly downtime and ensuring optimal sealing and reliability.
6. Computational Modeling and Simulation:
– Computational modeling and simulation techniques have played a significant role in advancing hydraulic cylinder sealing and reliability. These tools enable engineers to analyze and optimize seal designs, fluid flow dynamics, and contact stresses. By simulating various operating conditions, potential issues such as seal extrusion, wear, or leakage can be identified and mitigated early in the design phase, resulting in improved sealing performance and enhanced reliability.
7. Systematic Maintenance Practices:
– Advances in hydraulic cylinder technology have also emphasized the importance of systematic maintenance practices to ensure sealing and overall system reliability. Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of seals, as well as routine system flushing and filtration, help prevent premature seal failure and optimize sealing performance. Implementing preventive maintenance schedules and adhering to recommended service intervals contribute to extended seal life and enhanced reliability.
In summary, advancements in hydraulic cylinder technology have led to significant improvements in sealing and reliability. High-performance sealing materials, enhanced seal designs, integrated seal and bearing systems, advanced coatings and surface treatments, sealing system monitoring and diagnostics, computational modeling and simulation, and systematic maintenance practices have all played key roles in achieving optimal sealing performance and increased reliability. These advancements have resulted in more efficient and dependable hydraulic systems, minimizing leakage, wear, and failure of seals, and ultimately improving the overall performance and longevity of hydraulic cylinders in diverse applications.
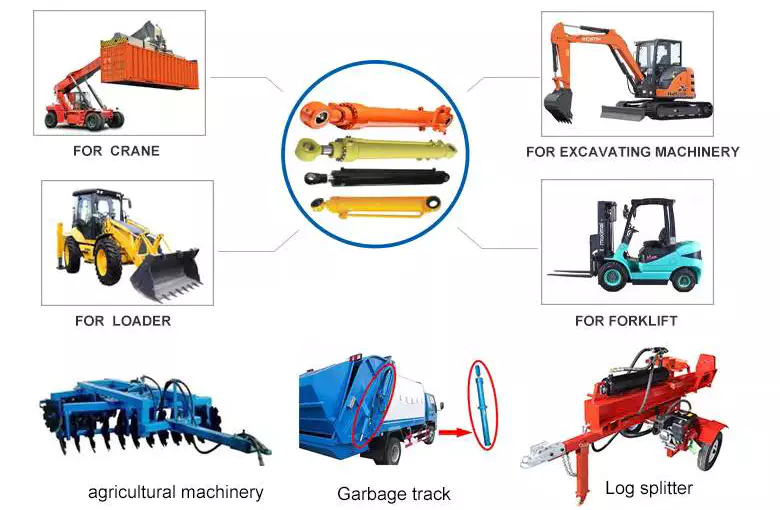
Integration of Hydraulic Cylinders with Equipment Requiring Rapid and Dynamic Movements
Hydraulic cylinders can indeed be integrated with equipment that requires rapid and dynamic movements. While hydraulic systems are generally known for their ability to provide high force and precise control, they can also be designed and optimized for applications that demand fast and dynamic motion. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders can be integrated with such equipment:
- High-Speed Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic cylinders can be part of high-speed hydraulic systems designed specifically for rapid and dynamic movements. These systems incorporate features such as high-flow valves, optimized hydraulic circuitry, and responsive control systems. By carefully engineering the system components and hydraulic parameters, it is possible to achieve the desired speed and responsiveness, enabling the equipment to perform rapid movements.
- Valve Control: The control of hydraulic cylinders plays a crucial role in achieving rapid and dynamic movements. Proportional or servo valves can be used to precisely control the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the cylinder. These valves offer fast response times and precise flow control, allowing for rapid acceleration and deceleration of the cylinder’s piston. By adjusting the valve settings and optimizing the control algorithms, equipment can be designed to execute dynamic movements with high speed and accuracy.
- Optimized Cylinder Design: The design of hydraulic cylinders can be optimized to facilitate rapid and dynamic movements. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys or composite materials, can be used to reduce the moving mass of the cylinder, enabling faster acceleration and deceleration. Additionally, the cylinder’s internal components, such as the piston and seals, can be designed for low friction to minimize energy losses and enhance responsiveness. These design optimizations contribute to the overall speed and dynamic performance of the equipment.
- Accumulator Integration: Hydraulic accumulators can be integrated into the system to enhance the dynamic capabilities of hydraulic cylinders. Accumulators store pressurized hydraulic fluid, which can be rapidly released to supplement the flow from the pump during high-demand situations. This stored energy can provide an extra boost of power, allowing for faster and more dynamic movements. By strategically sizing and configuring the accumulator, the system can be optimized for the specific rapid and dynamic requirements of the equipment.
- System Feedback and Control: To achieve precise and dynamic movements, hydraulic systems can incorporate feedback sensors and advanced control algorithms. Position sensors, such as linear potentiometers or magnetostrictive sensors, provide real-time position feedback of the hydraulic cylinder. This information can be used in closed-loop control systems to maintain precise positioning and execute rapid movements. Advanced control algorithms can optimize the control signals sent to the valves, ensuring smooth and dynamic motion while minimizing overshooting or oscillations.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders can be integrated with equipment that requires rapid and dynamic movements by utilizing high-speed hydraulic systems, employing responsive valve control, optimizing cylinder design, integrating accumulators, and incorporating feedback sensors and advanced control algorithms. These measures enable hydraulic systems to deliver the speed, responsiveness, and precision necessary for equipment operating in dynamic environments. By leveraging the capabilities of hydraulic cylinders, manufacturers can design and integrate systems that meet the requirements of applications demanding rapid and dynamic movements.

How do hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion using hydraulic fluid?
Hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of fluid mechanics, specifically Pascal’s law, in conjunction with the properties of hydraulic fluid. The process involves the conversion of hydraulic energy into mechanical force and linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders achieve this:
1. Pascal’s Law:
– Hydraulic cylinders operate based on Pascal’s law, which states that when pressure is applied to a fluid in a confined space, it is transmitted equally in all directions. In the context of hydraulic cylinders, this means that when hydraulic fluid is pressurized, the force is evenly distributed throughout the fluid and transmitted to all surfaces in contact with the fluid.
2. Hydraulic Fluid and Pressure:
– Hydraulic systems use a specialized fluid, typically hydraulic oil, as the working medium. This fluid is stored in a reservoir and circulated through the system by a hydraulic pump. The pump pressurizes the fluid, creating hydraulic pressure that can be controlled and directed to various components, including hydraulic cylinders.
3. Cylinder Design and Components:
– Hydraulic cylinders consist of several key components, including a cylindrical barrel, a piston, a piston rod, and various seals. The barrel is a hollow tube that houses the piston and allows for fluid flow. The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers: the rod side and the cap side. The piston rod extends from the piston and provides a connection point for external loads. Seals are used to prevent fluid leakage and maintain hydraulic pressure within the cylinder.
4. Fluid Input and Motion:
– To generate force and motion, hydraulic fluid is directed into one side of the cylinder, creating pressure on the corresponding surface of the piston. This pressure is transmitted through the fluid to the other side of the piston.
5. Force Generation:
– The force generated by a hydraulic cylinder is a result of the pressure applied to a specific surface area of the piston. The force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder can be calculated using the formula: Force = Pressure × Area. The area is determined by the diameter of the piston or the piston rod, depending on which side of the cylinder the fluid is acting upon.
6. Linear Motion:
– As the pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, it generates a force that moves the piston in a linear direction within the cylinder. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, which extends or retracts accordingly. The piston rod can be connected to external components or machinery, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks, such as lifting, pushing, pulling, or controlling mechanisms.
7. Control and Regulation:
– The force and motion generated by hydraulic cylinders can be controlled and regulated by adjusting the flow of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. By regulating the flow rate, pressure, and direction of the fluid, the speed, force, and direction of the cylinder’s movement can be precisely controlled. This control allows for accurate positioning, smooth operation, and synchronization of multiple cylinders in complex machinery.
8. Return and Recirculation of Fluid:
– After the hydraulic cylinder completes its stroke, the hydraulic fluid on the opposite side of the piston needs to be returned to the reservoir. This is typically achieved through hydraulic valves that control the flow direction, allowing the fluid to return and be recirculated in the system for further use.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of Pascal’s law. Pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, creating force that moves the piston in a linear direction. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks. By controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and motion of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely regulated, contributing to their versatility and wide range of applications in machinery.

editor by CX 2023-11-18